|
The discovery of carbon dioxide (CO2) in several sources was reported in 1989 by
d'Hendecourt et al. using instrumentation
on the IRAS spacecraft. As a molecule
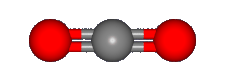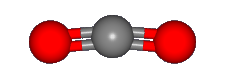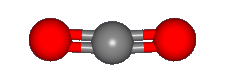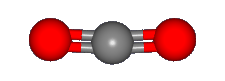
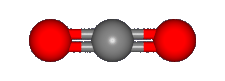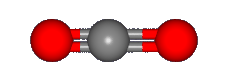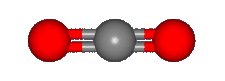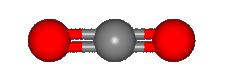
without a permanent dipole moment, CO2 was identified via one of its characteristic vibrational
features, the bending mode shown, rather than by rotational spectroscopy. Also unusual is that this feature
is observed in
icy grain mantles
rather than in the gas phase.
Carbon dioxide is a well-known
terrestrial molecule. It is a by-product of metabolism expelled in animal
respiration. It is a principal
greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. Frozen, it is
known as dry ice.
Carbon dioxide has a second mode that can also be seen in the infrared, the asymmetric stretching
mode shown below.
|